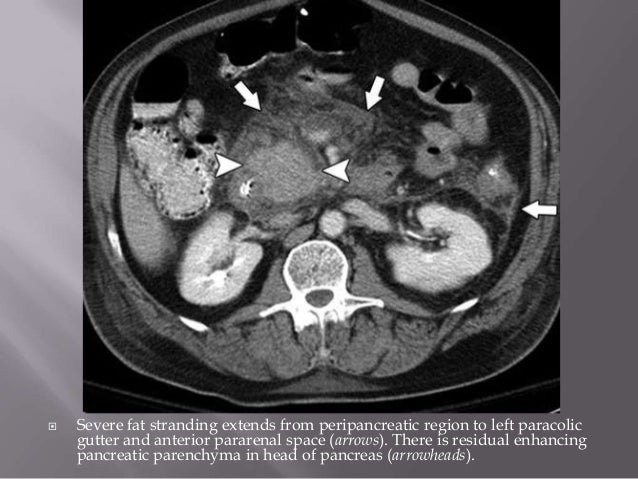
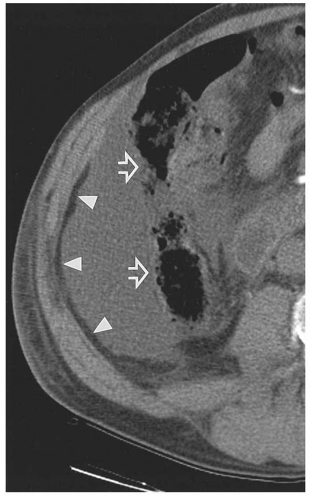
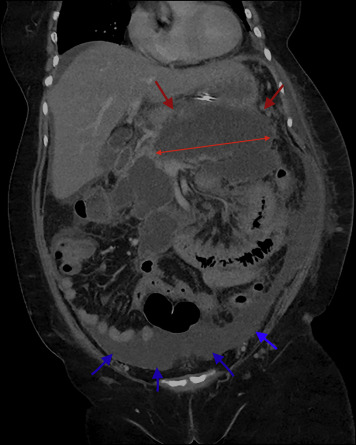
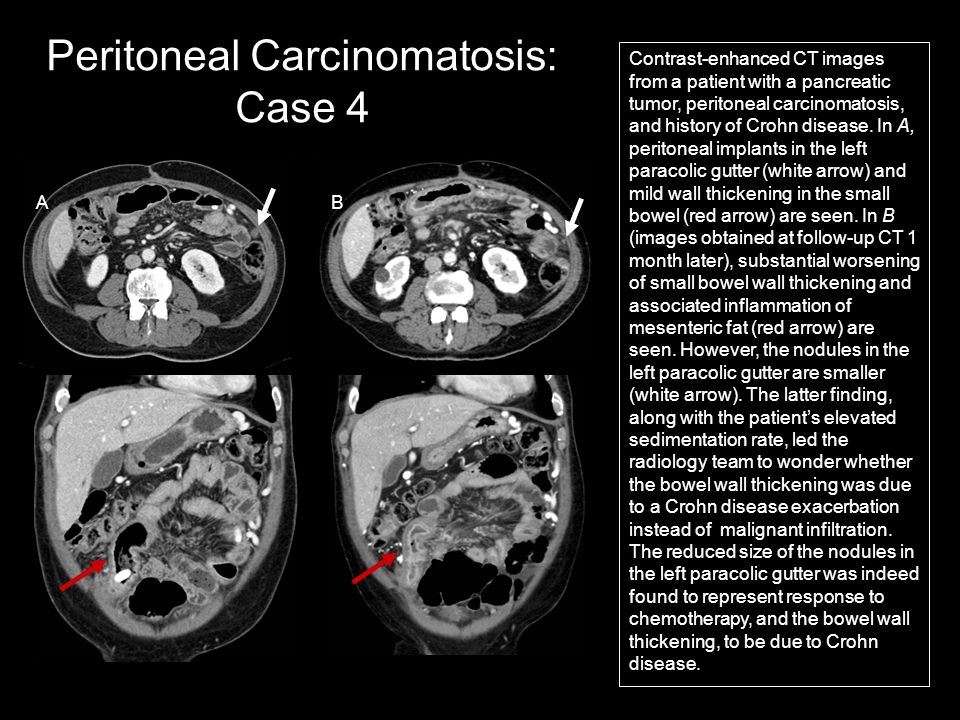
Paracolic Gutter Fluid Ct

The right lateral paracolic gutter.
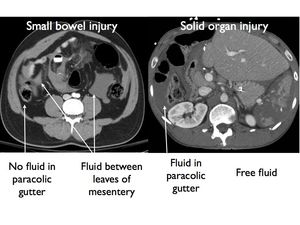
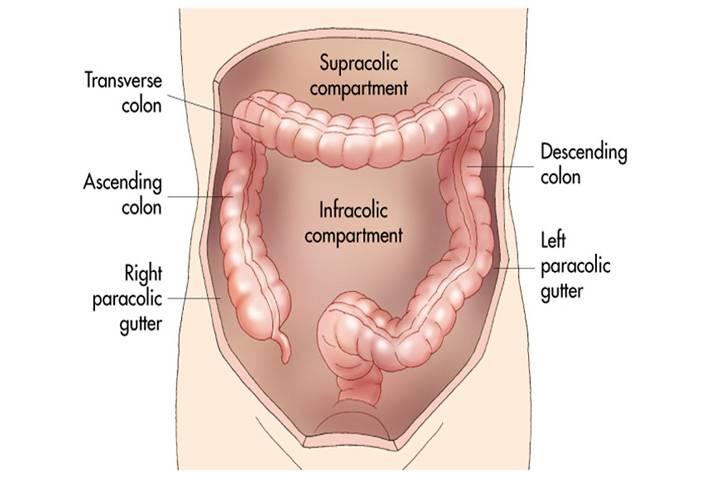
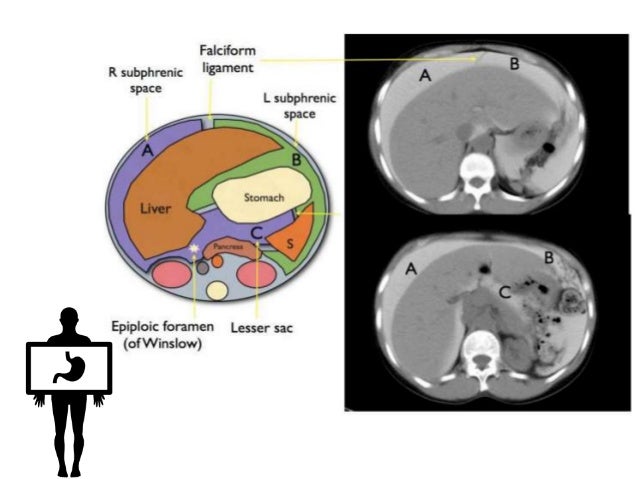
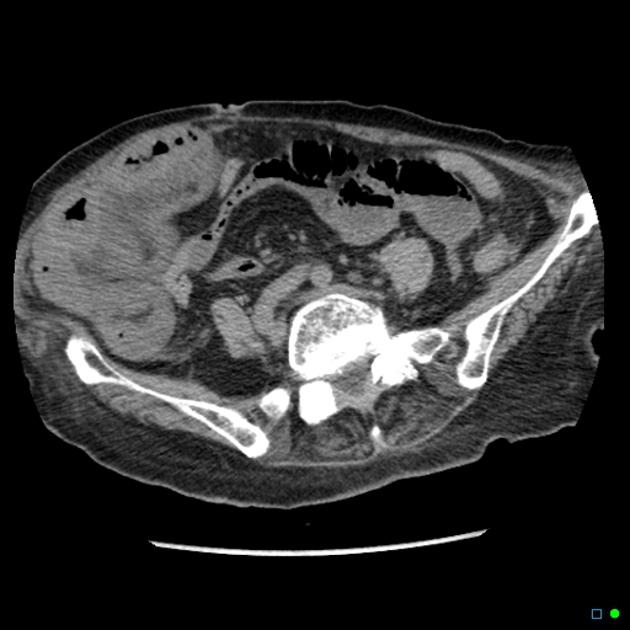
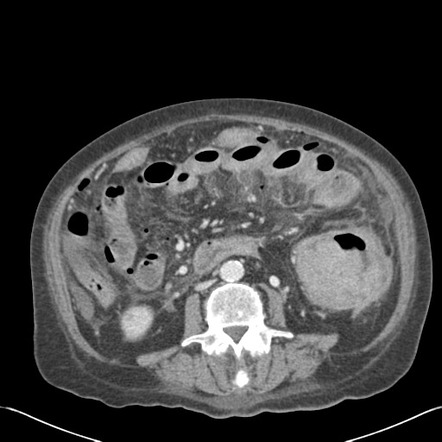
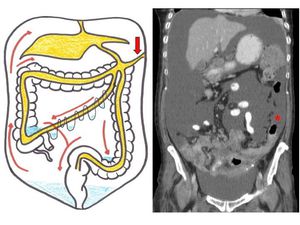
Paracolic gutter fluid ct. The right and left paracolic gutters both lies on the lateral side of posterior abdominal wall alongside the ascending and descending colon are the peritoneal recesses. The right paracolic gutter is much larger than the left one and thus allows more fluid to pass through. Blood in the peritoneal cavity from trauma is often first seen in the right paracolic gutter at the inferior tip of the liver. Compared with computed tomography ct other advantages of us are its lack of ionizing radiation and lower cost.
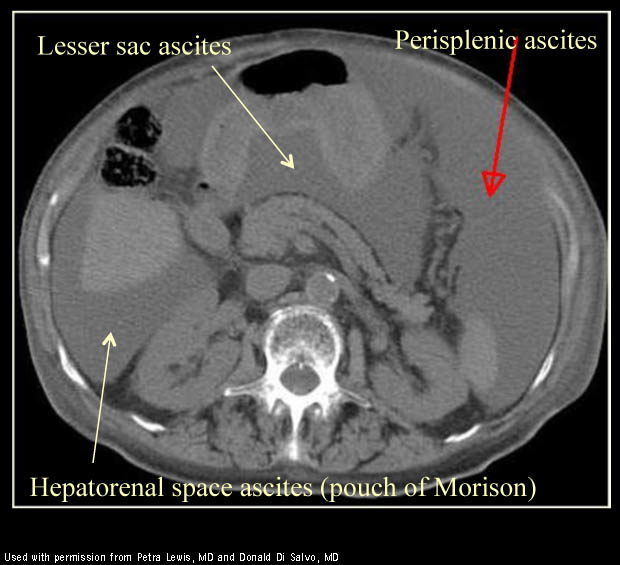
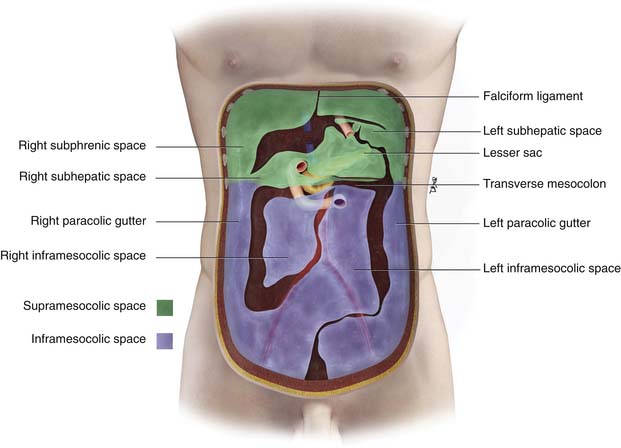
Small amounts of ascitic fluid localize in the right perihepatic space the posterior subhepatic space i e morison s pouch and the pouch of douglas. The left lateral paracolic gutter. The left medial paracolic gutter. It can be divided into two unequal spaces posteriorly by the mesentery of the small bowel as it runs from the duodenojejunal flexure in the left upper quadrant to the ileocecal valve in the right lower quadrant.
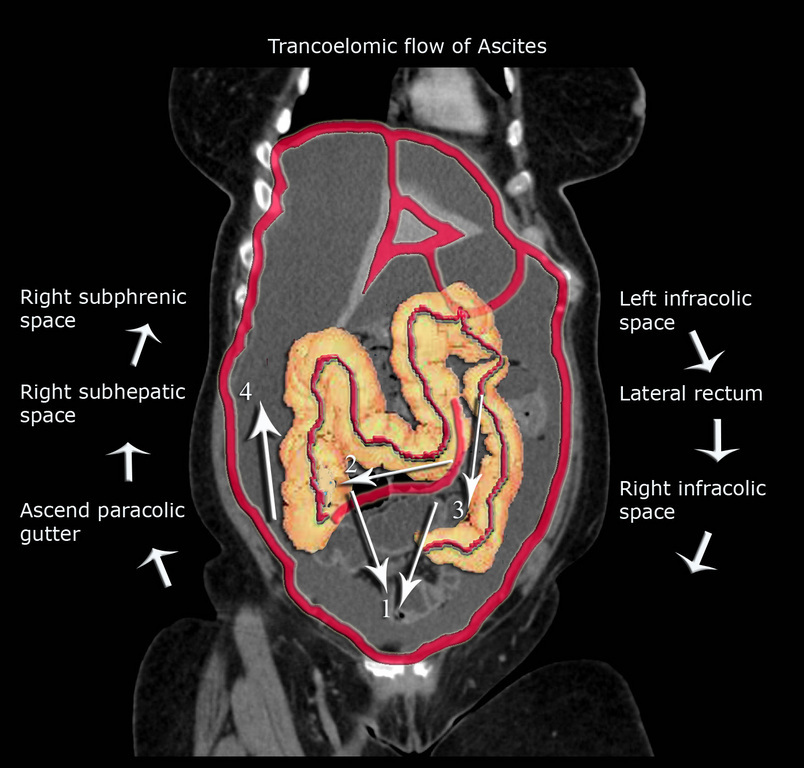
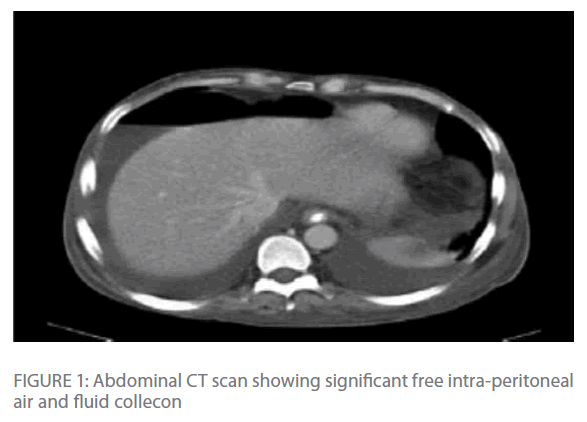
Ascites is the collection of free fluid in the peritoneal cavity normally the peritoneal cavity contain small amount of serous fluid for lubrication less than 100 ml free fluid exceeding this amount considered ascites ascites may result from variety of medical surgical causes clinically detectable ascites when its amount exceeding 1500 ml and. The main paracolic gutter lies lateral to the colon on each side. Fluid flow and stasis is dependent on gravity changes in intra abdominal pressure and peritoneal reflections. When larger amounts of ascites are present the fluid accumulates in the paracolic gutters causing progressive centralization of bowel loops.
A less obvious medial paracolic gutter may be formed especially on the right side if the colon. Fluid may sit within the peritoneal space or paracolic gutters or may be interposed between bowel loops or around solid organs e g. The right paracolic gutter is larger than the left and. Back ground and purposes.
B coronal ct image obtained in a 51 year old man shows the supramesocolic spaces outlined by dialysate solution. The inframesocolic space is the peritoneal space below the root of the transverse mesocolon the supramesocolic space lies above the transverse mesocolon s root. Ascites is well demonstrated by ct. Areas of preferential fluid stasis include the pouch of douglas the right lower quadrant at the termination of the small bowel mesentery superior aspect of the sigmoid mesentery and the right paracolic gutter.
Of the small amount of normal peritoneal fluid. The right and left paracolic gutters are peritoneal recesses on the posterior abdominal wall lying alongside the ascending and descending colon. Paracolic gutters function to drain fluid that leaks from the colon such as infectious matter pus or bile and to prevent infection or damage to the outer margin of the colon this drainage occurs in much the same way that the gutters on a house draw the rain off the roof. It can be compared to fluid in the gallbladder or stomach.